WHAT IS MATTER?
Definition: Anything that has mass and takes up space
MAIN CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER
Matter is classified into TWO main categories:
1. PURE SUBSTANCES
Characteristics:
- Made of the same particles
- Homogeneous (uniform throughout)
- Have fixed composition
2. MIXTURES
Characteristics:
- Made up of two or more different particles
- Can be homogeneous or heterogeneous
- Variable composition
PURE SUBSTANCES
Pure substances are divided into:
A. ELEMENTS
Definition: Made up of one type of atom
Properties:
- Cannot be broken down by any physical or chemical means
- Simplest form of matter
- Each element has unique properties
Examples:
- Au (Gold)
- Ag (Silver)
- O₂ (Oxygen)
- H₂ (Hydrogen)
B. COMPOUNDS
Definition: Made up of two or more elements that are chemically combined
Properties:
- Chemical process is required to break them apart
- Have different properties from constituent elements
- Fixed ratio of elements
Examples:
- H₂O (Water)
- NaCl (Sodium chloride/Salt)
- CO₂ (Carbon dioxide)
MIXTURES
Mixtures are classified into THREE main types:
1. SOLUTION (Homogeneous Mixture)
Properties:
- Homogeneous mixture
- One particle completely dissolves in another
- Uniform appearance throughout
- Cannot see individual components
Examples:
- Salt and water
- Sugar and water
- Air (mixture of gases)
2. SUSPENSIONS (Heterogeneous Mixture)
Properties:
- Heterogeneous mixture
- The solid is suspended in a liquid
- Cloudy appearance
- Particles can settle over time
- Can be separated by filtration
Examples:
- Starch and water
- Muddy water
- Chalk powder in water
3. MECHANICAL MIXTURE (Heterogeneous Mixture)
Properties:
- Heterogeneous mixture
- Particles do not mix at all
- Can see all different parts clearly
- Easy to separate physically
Examples:
- Pizza
- Salad
- Salt and pepper
- Sand and iron filings
SPECIAL TYPES OF MIXTURES
ALLOY
Definition: Homogeneous mixture of two or more metals
Properties:
- Solid solution of metals
- Uniform composition
- Different properties from pure metals
Examples:
- Brass: Copper + Zinc
- Bronze: Copper + Tin
- Solder: Lead + Tin
- Steel: Iron + Carbon
COLLOID
Definition: Heterogeneous mixture but looks homogeneous (particles are microscopically dispersed within another substance)
Properties:
- Intermediate between solution and suspension
- Particles are larger than in solution but smaller than in suspension
- Shows Tyndall effect (scattering of light)
Examples:
- Gel (solid-liquid mix)
- Milk
- Blood
- Fog
- Smoke
KEY DEFINITIONS FOR EXAMS
Homogeneous: A substance or mixture that has uniform appearance and composition throughout
Heterogeneous: A substance or mixture of visibly different components or phases (solid, liquid, or gas)
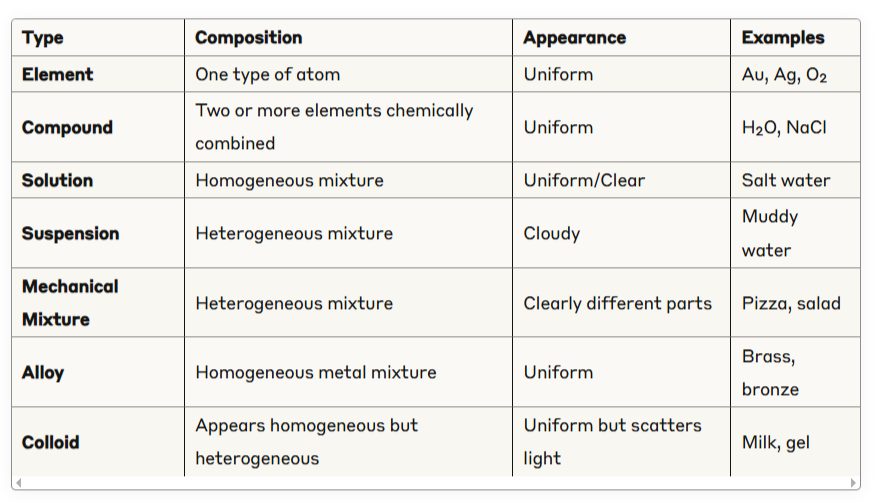
SUMMARY TABLE FOR QUICK REVISION
EXAM TIPS
Remember the hierarchy:
MATTER
├── Pure Substances
│ ├── Elements (1 type of atom)
│ └── Compounds (2+ elements, chemically combined)
└── Mixtures
├── Homogeneous (Solutions, Alloys)
└── Heterogeneous (Suspensions, Mechanical mixtures)Key Points to Remember:
- Pure substances have fixed composition
- Mixtures have variable composition
- Elements cannot be broken down chemically
- Compounds require chemical processes to separate
- Solutions are clear, suspensions are cloudy
- Mechanical mixtures have visible different parts
- Alloys are metal mixtures
- Colloids appear uniform but scatter light