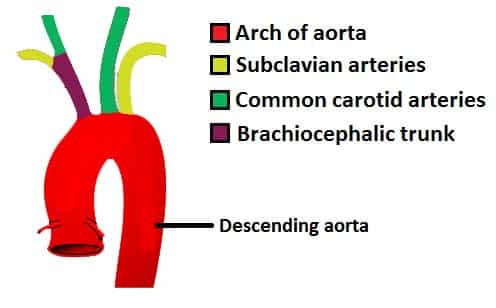
Introduction
- The aorta is the largest artery in the human body.
- It carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
- Acts as the main highway of blood circulation.
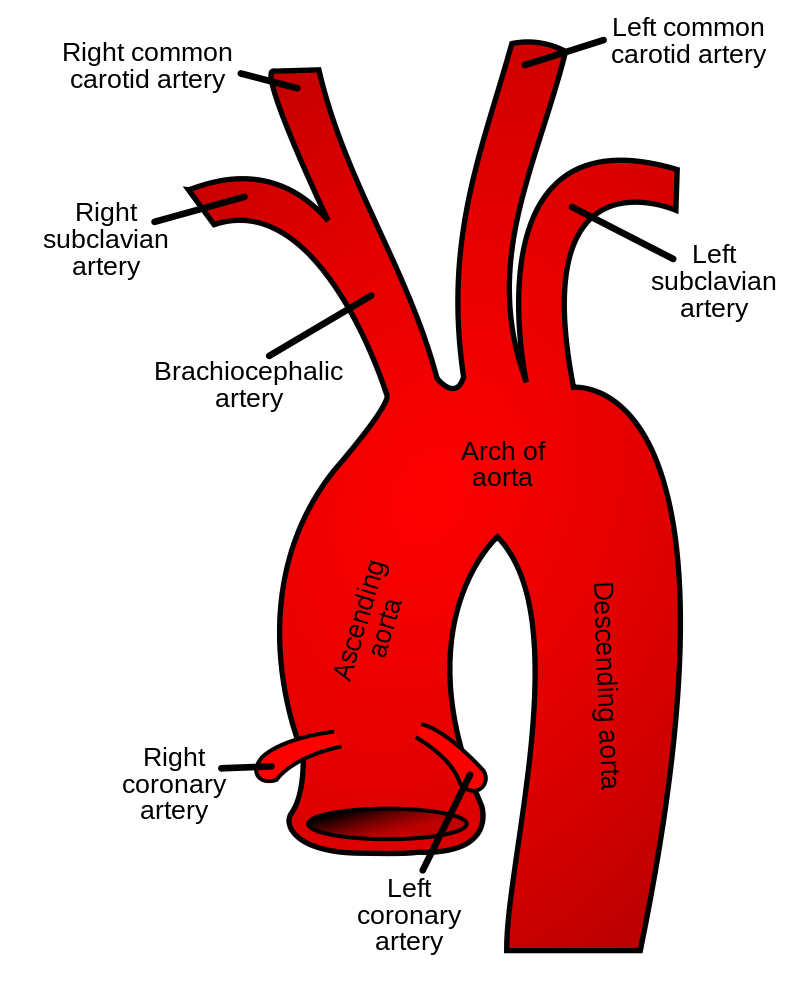
Key Functions of the Aorta
Main Blood Distributor
- Carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to all body parts.
- Supplies blood through its branches: ascending aorta, aortic arch, descending aorta.
Maintains Blood Pressure
- The aorta’s elastic walls expand when the heart pumps blood.
- Then they recoil, ensuring continuous blood flow even between heartbeats.
Branch Supply to Vital Organs
- Coronary arteries → supply the heart itself.
- Carotid arteries → supply the brain and head.
- Thoracic & abdominal branches → supply lungs, kidneys, digestive organs, and limbs.
Supports Systemic Circulation
- Systemic circulation = transport of oxygen-rich blood to the entire body.
- The aorta is the starting point of this circulation.
Real-Life Relevance
- Without the aorta’s function, body organs would lack oxygen & nutrients.
- Example: If blood flow in the aorta is blocked (like in aortic aneurysm), it can be life-threatening.
Quick Memory Tip (AORTA)
- ✓ A → Artery (largest)
- ✓ O → Oxygenated blood carrier
- ✓ R → Regulates blood flow/pressure
- ✓ T → Transports blood to organs
- ✓ A → Arches into branches for distribution